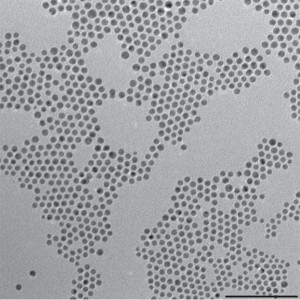
The excessive atmospheric carbon dioxide that is driving global climate change could be harnessed into a renewable energy technology that would be a win for both the environment and the economy. That is the lure of artificial photosynthesis in which the electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide is used to produce clean, green and sustainable fuels. However, finding a catalyst for reducing carbon dioxide that is highly selective and efficient has proven to be a huge scientific challenge.
Working at the Molecular Foundry through a user project, Peidong Yang led a study in which bimetallic nanoparticles of gold and copper were used as the catalyst for the carbon dioxide reduction. The results experimentally revealed for the first time the critical influence of the electronic and geometric effects in the reduction reaction.