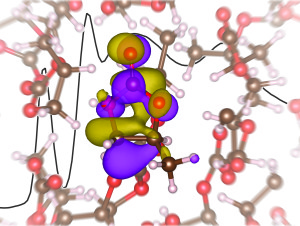
Foundry staff and users found surprising results in the first X-ray absorption spectroscopy study of a model lithium electrolyte and in so doing, may have found a path towards improved lithium-ion batteries.
Commercial lithium-ion batteries contain a liquid electrolyte comprising a lithium salt dissolved in an alkyl carbonate solvent system. There’s disagreement in the battery industry on the nature of the local solvation environment of lithium ions in these solutions, a critical issue because the desolvation of the ions as they move through the negative electrode is believed to limit the electrical power that can be made available.
The team’s results contradicts numerous theoretical studies. Their work indicates that to design better performing electrolytes, future research will need to move beyond the existing models.