Scientific Achievement
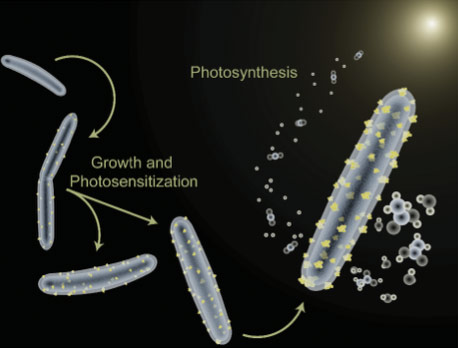
Molecular Foundry users induced the nonphotosynthetic, CO2 reducing bacterium M. thermoacetica to precipitate cadmium sulfide nanoparticles which serve as light harvesters to enable photosynthetic production of acetic acid.
Significance and Impact
This hybrid inorganic-biological system combines the high efficiency light absorption of inorganic semiconductors with the catalytic power of biology, opening up a new parameter space to explore in solar-to-chemical research.
Research Details
- M. thermoacetica-CdS shows stable photosynthesis and maintains cell viability over several days under simulated day/night cycles.
- Biosynthesis of CdS nanoparticles from simple components offers a cheap, scalable approach at mild conditions.