Scientific Achievement
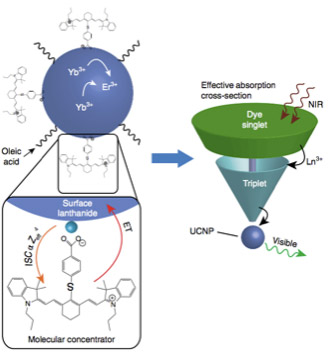
An international team of scientists led by Foundry researchers has discovered the mechanism of how coating nanoparticles with organic dyes greatly enhances their ability to capture near-infrared light and to reemit it in the visible light spectrum.
Significance and Impact
This study is a breakthrough in the design and function of nanoparticles that could make solar panels more efficient by converting light usually missed by solar cells into usable energy.
Research Details
- The researchers found that the organic dye itself amplifies the brightness of the reemitted light about 33,000-fold, and its efficiency in converting light by about 100 times.
- The proximity of the dyes to the lanthanides in the nanoparticles enhances the presence of a dye state known as a “triplet,” which then transfers its energy to the lanthanides more efficiently.
- Increasing the concentration of lanthanide metals in the nanoparticles increased the triplet effect and improved the nanoparticles’ light-converting properties.
- The dyes act as molecular-scale solar concentrators, funneling energy from near-infrared photons into the nanoparticles, but are themselves transparent to visible light and allow other usable light to pass.