Scientific Achievement
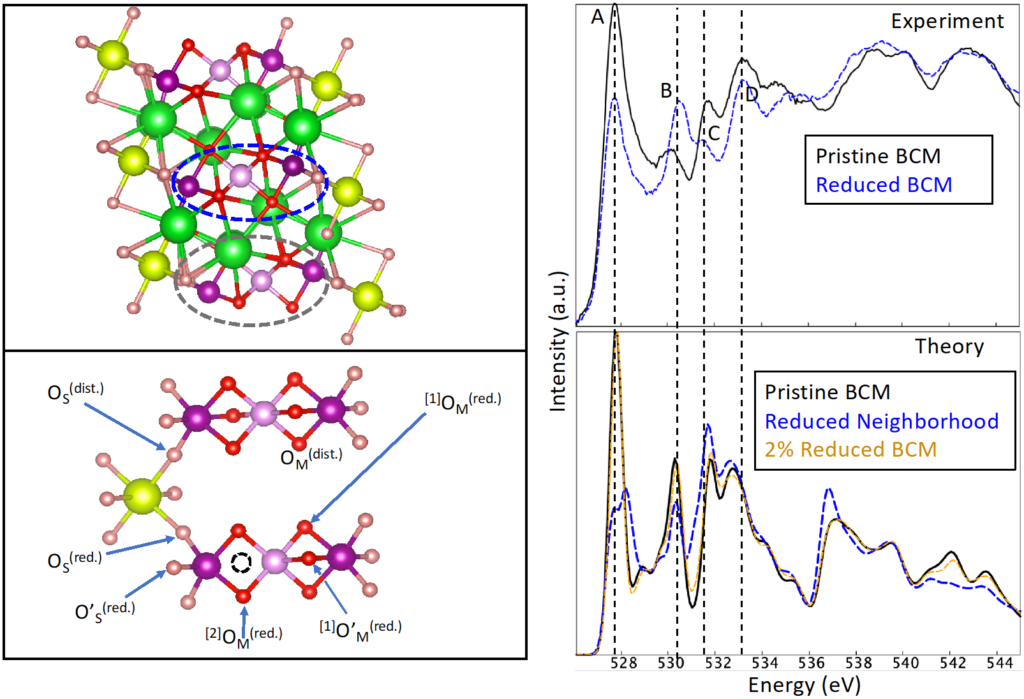
Identification of X-ray spectral signatures of oxygen vacancies and their location in a promising water-splitting oxide BaCe0.25Mn0.75O3−δ (BCM) for H2 production.
Significance and Impact
This study paves the way for the investigation of the working mechanism of BCM and for computational and experimental efforts aimed at design and discovery of efficient water-splitting oxides.
Research Details
- The team performed detailed theoretical analysis (DFT) to model reduction by oxygen vacancy formation and found O vacancies reduce Mn sites rather than Ce.
- Simulated X-ray absorption spectra validate this model by comparison with experimental data.
- Connection to atomic structure highlights challenges in vacancy mobility/migration that limit performance.