Scientific Achievement
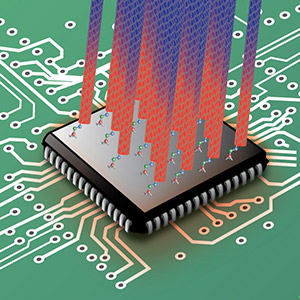
In a User project with Intel, Foundry scientists have shown that the use of short organic molecules that form covalent bonds between metal surfaces and vertically aligned carbon nanotubes (CNTs) leads to a six-fold reduction in thermal interface resistance.
Significance and Impact
Thermal interface resistance is the bottleneck that limits the performance of highly conductive CNTs for heat control in numerous technologies including microprocessors. Covalent bonds across the interface can break this bottleneck.
Research Details
- CNTs have unmatched thermal conductivity but interact only weakly with most other materials, leading to high thermal interface resistance.
- Covalently bonding CNT arrays to metal surfaces using aminopropyl-trialkoxy-silane (APS) or cysteamine increases the interaction strength and the efficiency of heat transport. .