Scientific Achievement
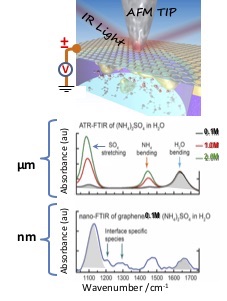
Determined the structure and speciation of a (NH3)2SO4 aq. electrolyte within a few nm of a graphene electrode by plasmonic tip-enhanced IR under in-operando conditions.
Significance and Impact
Knowledge of the structure and composition of nanometer-thin solid-liquid interface regions is key for understanding corrosion, batteries, bio- and electro-chemical phenomena.
Research Details
- The EDL and Gouy-Chapman layers are highly enriched in sulfate SO4=, at positive bias.
- The sharp AFM tip was located outside of a graphene electrode that encloses the electrolyte inside a cell.
- FTIR with nanometer spatial resolution was obtained in the x, y and z directions, making it possible to determine the structure of solid-liquid interfaces under bias, and in-operando conditions.