Article adapted from the Berkeley Lab Newscenter
A team of Foundry users has developed a new technique for fabricating tiny circuits from ultrathin materials for next-generation electronics, such as rewritable, low-power memory circuits. Their findings were reported in the journal Nature Electronics.
Using the Foundry’s nanofabrication facility, the researchers prepared two different 2D devices known as van der Waals heterostructures: one by sandwiching graphene between two layers of boron nitride; and another by sandwiching molybdenum disulfide.
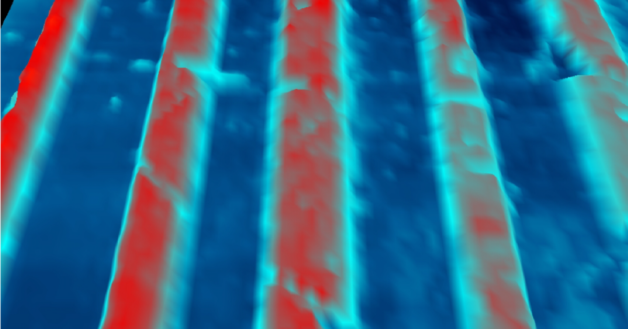
When applying a fine electron beam to the boron-nitride “sandwiches,” the researchers demonstrated that they can “write” nanoscale conducting channels, or nanocircuits, into the core “active” layer by controlling the intensity of electron beam exposure while properly controlling a back-gate electric field.
When written into the graphene or molybdenum disulfide layer, these nanocircuits allow high densities of electrons, or quasiparticles called holes, to accumulate and move through the semiconductor along narrow predetermined tracks at ultrahigh speeds with few collisions – like cars racing through a freeway within inches of each other without crashing or stalling.
The researchers also found that reapplying the electron beam with a special back-gate to the 2D materials can erase nanocircuits that have already been written – or write additional or different circuits in the same device, which suggests that the technique has great potential for next-generation reconfigurable 2D electronics.
Importantly, the researchers demonstrated that the material’s conducting states and ultrahigh electronic mobility persists even after the electron beam and the back-gate have been removed. This finding is critical to many applications, including energy-efficient nonvolatile memory devices that do not require constant power to retain data.